What is a Graph Database?
|
Important - page not maintained
This page is no longer being maintained and its content may be out of date. For the latest guidance, please visit the Getting Started Manual . |
Beginner
A graph database stores nodes and relationships instead of tables, or documents. Data is stored just like you might sketch ideas on a whiteboard. Your data is stored without restricting it to a pre-defined model, allowing a very flexible way of thinking about and using it.
Why Graph Databases?
We live in a connected world, and understanding most domains requires processing rich sets of connections to understand what’s really happening. Often, we find that the connections between items are as important as the items themselves.
How else do people do this today? While existing relational databases can store these relationships, they navigate them with expensive JOIN operations or cross-lookups, often tied to a rigid schema.
It turns out that "relational" databases handle relationships poorly.
In a graph database, there are no JOINs or lookups.
Relationships are stored natively alongside the data elements (the nodes) in a much more flexible format.
Everything about the system is optimized for traversing through data quickly; millions of connections per second, per core.
Graph databases address big challenges many of us tackle daily. Modern data problems often involve many-to-many relationships with heterogeneous data that sets up needs to:
-
Navigate deep hierarchies,
-
Find hidden connections between distant items, and
-
Discover inter-relationships between items.
Whether it’s a social network, payment networks, or road network you’ll find that everything is an interconnected graph of relationships. And when we want to ask questions about the real world, many questions are about the relationships rather than about the individual data elements.
The Property Graph Model
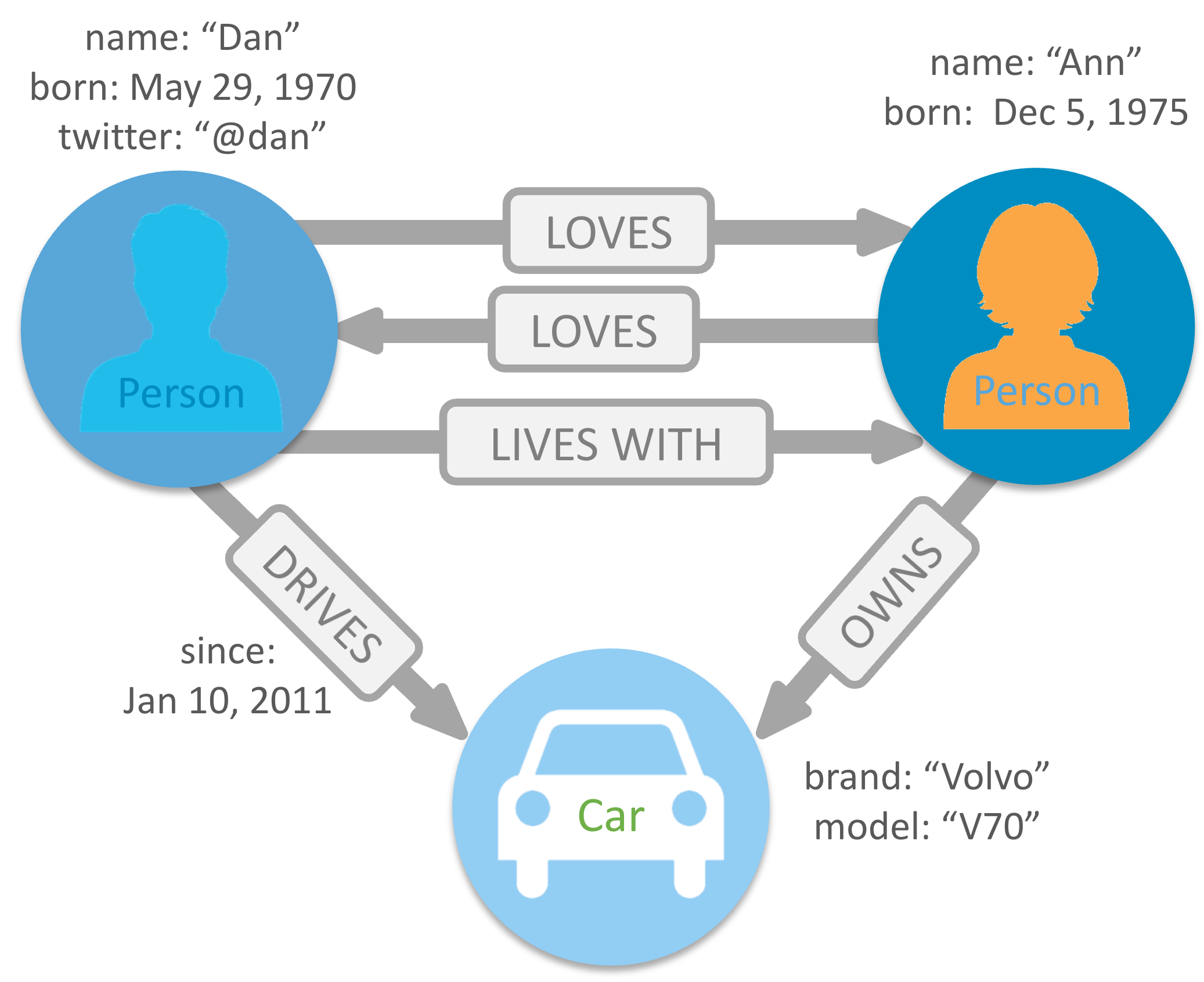
In Neo4j, information is organized as nodes, relationships, and properties.
Nodes are the entities in the graph.
-
Nodes can be tagged with labels, representing their different roles in your domain. (For example,
Person). -
Nodes can hold any number of key-value pairs, or properties. (For example,
name) -
Node labels may also attach metadata (such as index or constraint information) to certain nodes.
Relationships provide directed, named, connections between two node entities (e.g. Person LOVES Person).
-
Relationships always have a direction, a type, a start node, and an end node, and they can have properties, just like nodes.
-
Nodes can have any number or type of relationships without sacrificing performance.
-
Although relationships are always directed, they can be navigated efficiently in any direction.
If you’d like to learn more about any of these, you can read more about Graph Data Modeling.
What is Neo4j?
Neo4j is an open-source, NoSQL, native graph database that provides an ACID-compliant transactional backend for your applications that has been publicly available since 2007.
Neo4j is offered as a managed service via AuraDB. But you can also run Neo4j yourself with either Community Edition or Enterprise Edition. The Enterprise Edition includes all that Community Edition has to offer, plus extra enterprise requirements such as backups, clustering, and failover abilities. Neo4j is written in Java and Scala, and the source code is available on GitHub.
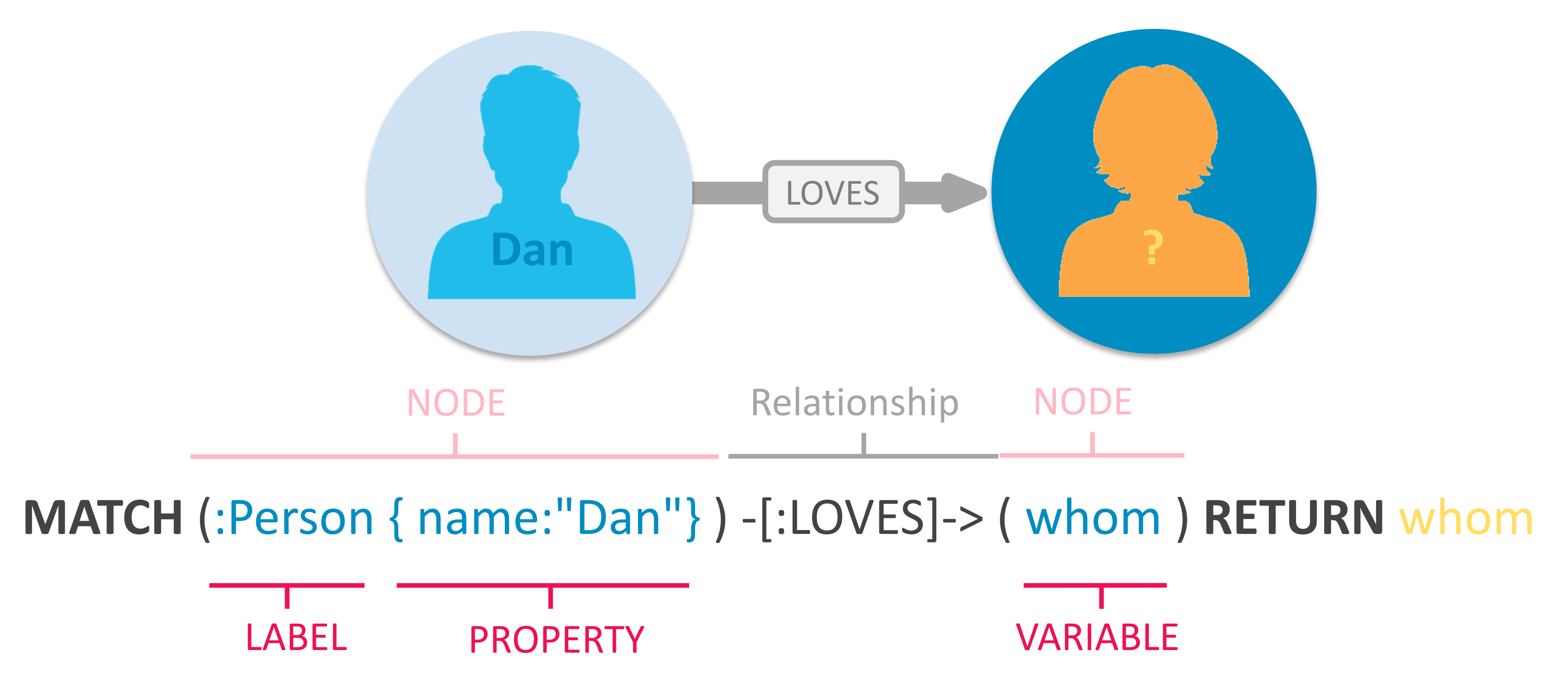
Neo4j is a native graph database, which means that it implements a true graph model all the way down to the storage level. The data isn’t stored as a "graph abstraction" on top of another technology, it’s stored just as you whiteboard it. This is important because it’s the reason why Neo4j outperforms other graphs and stays so flexible. Beyond the core graph, Neo4j provides what you’d expect out of a database; ACID transactions, cluster support, and runtime failover. This stability and maturity is why it’s been used in production scenarios for large enterprise workloads for years.
What makes Neo4j the easiest graph to work with?
-
Cypher, a declarative query language similar to SQL, but optimized for graphs. Now used by other databases like SAP HANA Graph and Redis graph via the openCypher project.
-
Constant time traversals in big graphs for both depth and breadth due to efficient representation of nodes and relationships. Enables scale-up to billions of nodes on moderate hardware.
-
Flexible property graph schema that can adapt over time, making it possible to materialize and add new relationships later to shortcut and speed up the domain data when the business needs change.
-
Drivers for popular programming languages, including Java, JavaScript, .NET, Python, and many more.
Where and How is Neo4j Used?
Neo4j is used today by thousands of startups, educational institutions, and large enterprises in all sectors including financial services, government, energy, technology, retail, and manufacturing. From innovative new technology to driving businesses, users are generating insights with graph, generating new revenue, and improving their overall efficiency.
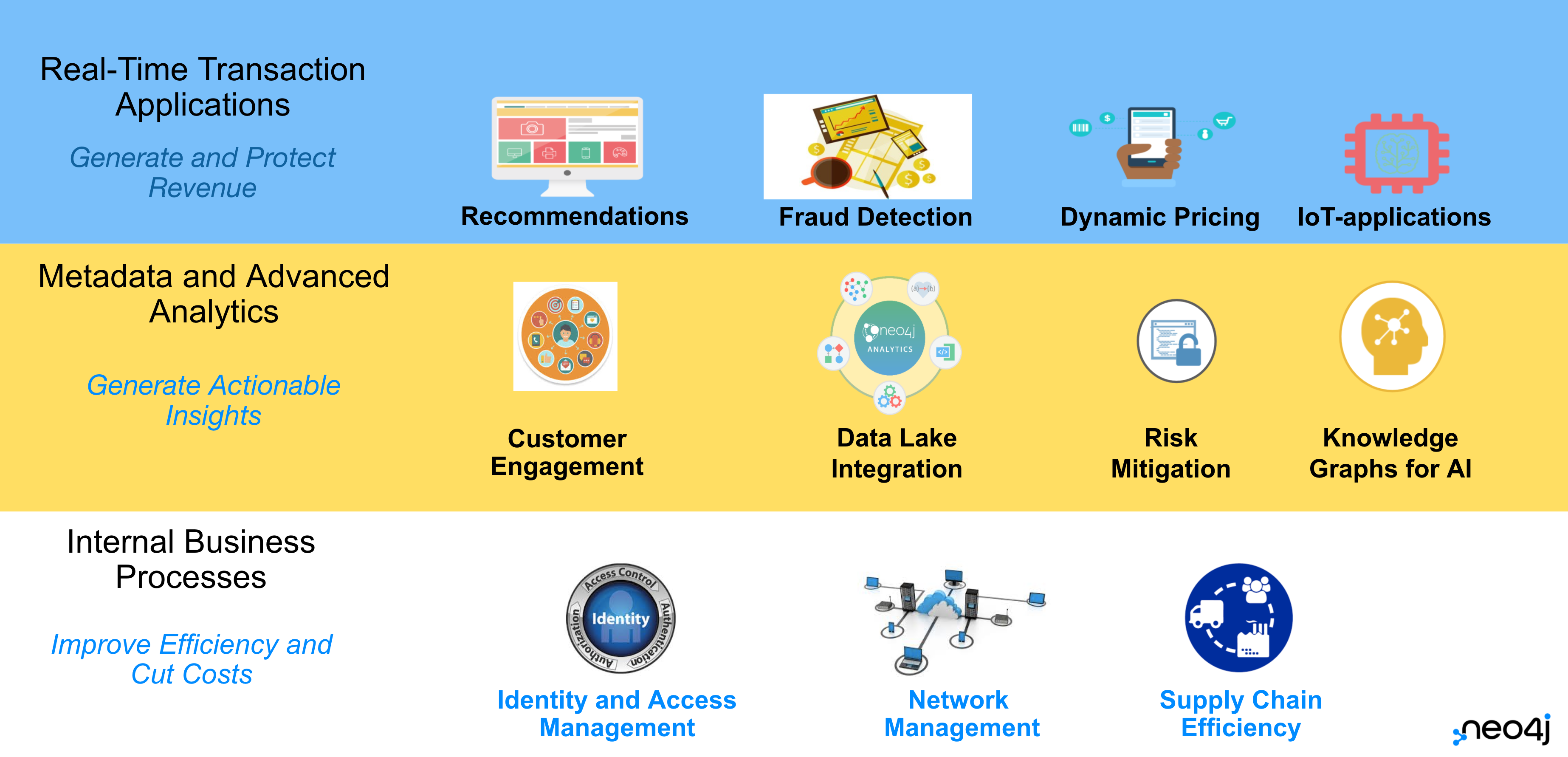
Learn more about different use cases and companies using them in the video below.
Learn with GraphAcademy
Neo4j Fundamentals
In this free course, we take you on a journey from 1736 Prussia for a brief history of graph theory, discuss the types of graphs you may see in the wild, and walk through an example dataset.
This course is designed for both beginners and non-technical audiences who are interested in learning more about Graphs and Neo4j.